
Contents
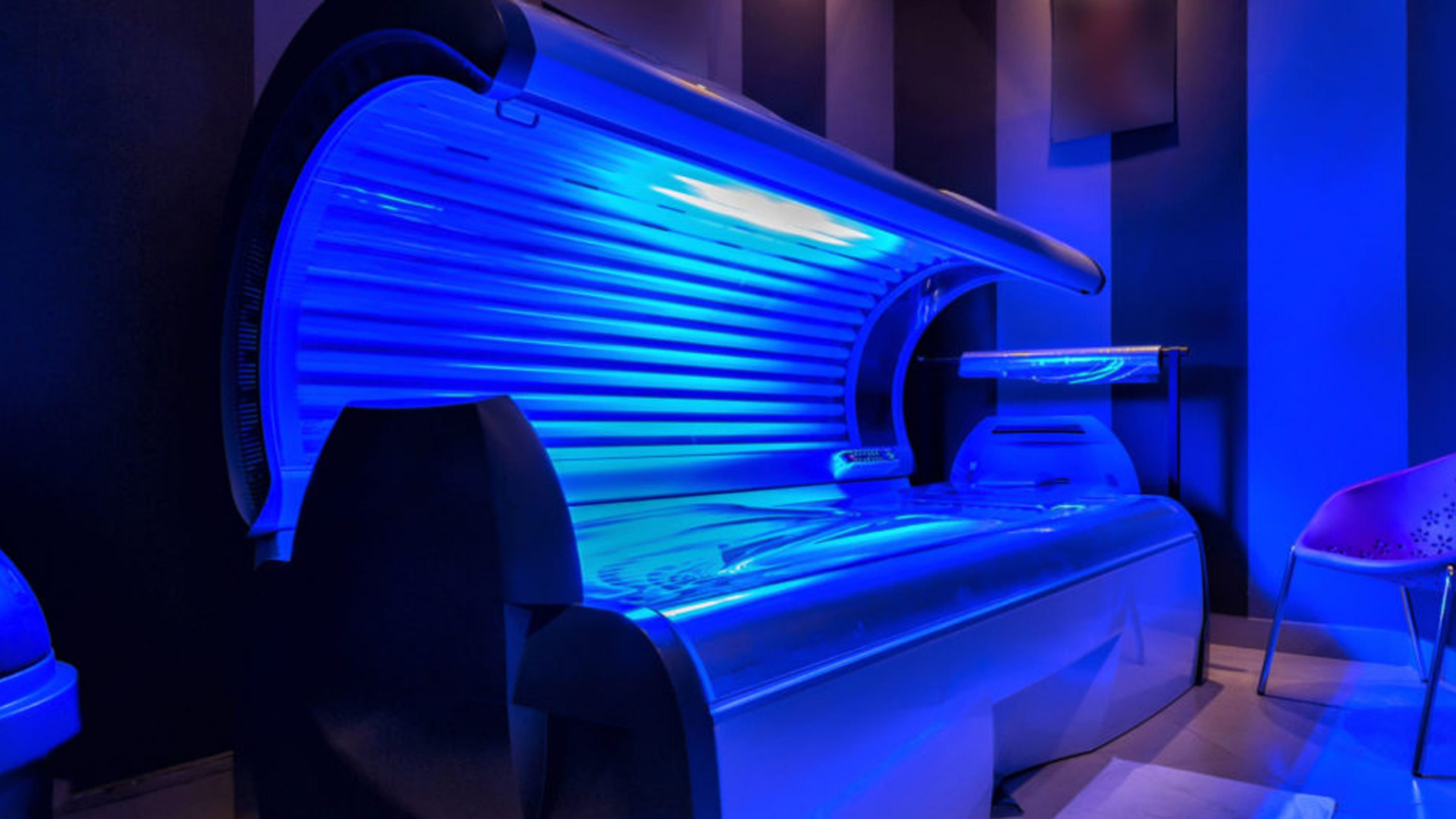
Bronze, healthy, golden skin from the Gods is gorgeous. If you’re after a “summer glow” but can’t get out into the sun then a tanning bed seems like the perfect solution. Or it does until you find out about tanning bed stats.
Till the late 2000s, when the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) updated the category of tanning beds from Group 2A (probably carcinogenic to humans) to Group 1 (carcinogenic to humans), tanning beds were fairly trendy.
Approximately 450,000 new cases of skin cancer are related to indoor tanning per year. In short, there’s no safe tanning bed. Up next we’re going to tell you how tanning beds actually are.
The DNA of your outer skin cells is harmed by ultraviolet (UV) rays, either from the sun or tanning beds. The damage is still done, whether your skin turns red or tans.
Moreover, indoor tanning, according to board-certified dermatologist Rachel Nazarian, MD, of Schweiger Dermatology Group in New York City, is more hazardous than outdoor tanning in the sun.
Tanning beds can release ultraviolet radiation at a 10 to 15 times greater than you’d get from sun exposure even at the peak of a sunny day. These increased levels of radiation can lead to more serious and greater damage to the skin cells.
Just like the sun, the explanation is that tanning beds, emit two forms of UV radiation: UVA and UVB rays.
Some risks of artificial UV exposure are listed below.
Indoor tanning should be discouraged for individuals of all ages. Use a self-tanning product that contains the active ingredient dihydroxyacetone (DHA) if you like the appeal of tanned skin.
You can find self-tanning products in various forms like lotions, foams, wipes, and sprays. Most of those are quick-acting and will give a darker appearance to your skin in a matter of hours.
You should not use tanning beds as your vitamin D source. An array of food options and dietary supplements can provide you with the D vitamin if you can’t get sun.
Vitamin D-rich foods include fish (particularly fatty fish), orange juice, milk, and several other dairy products. There are also some cereals containing high levels of vitamin D.
And if you really want that glow, just use a glowy foundation, it can do the job without submitting your skin to harmful rays.
Although this article focuses on the risks of tanning beds and indoor tanning, outdoor tanning is also not safe. Wear protective clothing if you are going to be in the sun – and that’s for every day even if it isn’t super sunny.
You are never too late to start safeguarding your skin from the sun and indoor tanning beds. Your body begins to heal some of the harmful effects of UV rays as soon as you start taking care.
This post was last modified on September 25, 2020 10:37 pm
Dry, fragile strands that flake and break off make it even harder to have a…
Life is too short to live between black and white, and we know this by…
If you’re a curly-haired girl, then you probably know the challenges behind managing that curly…
Big eyes, curled lashes, and thick brows are the perfect combination to make any women's…
It can be challenging to grow a full, glorious beard. When jumping right into bearded…
If you've ever encountered only a slight amount of frizz, a friend or two might…